Existing Patients
(949) 880-6638
New Patients
(949) 216-3427
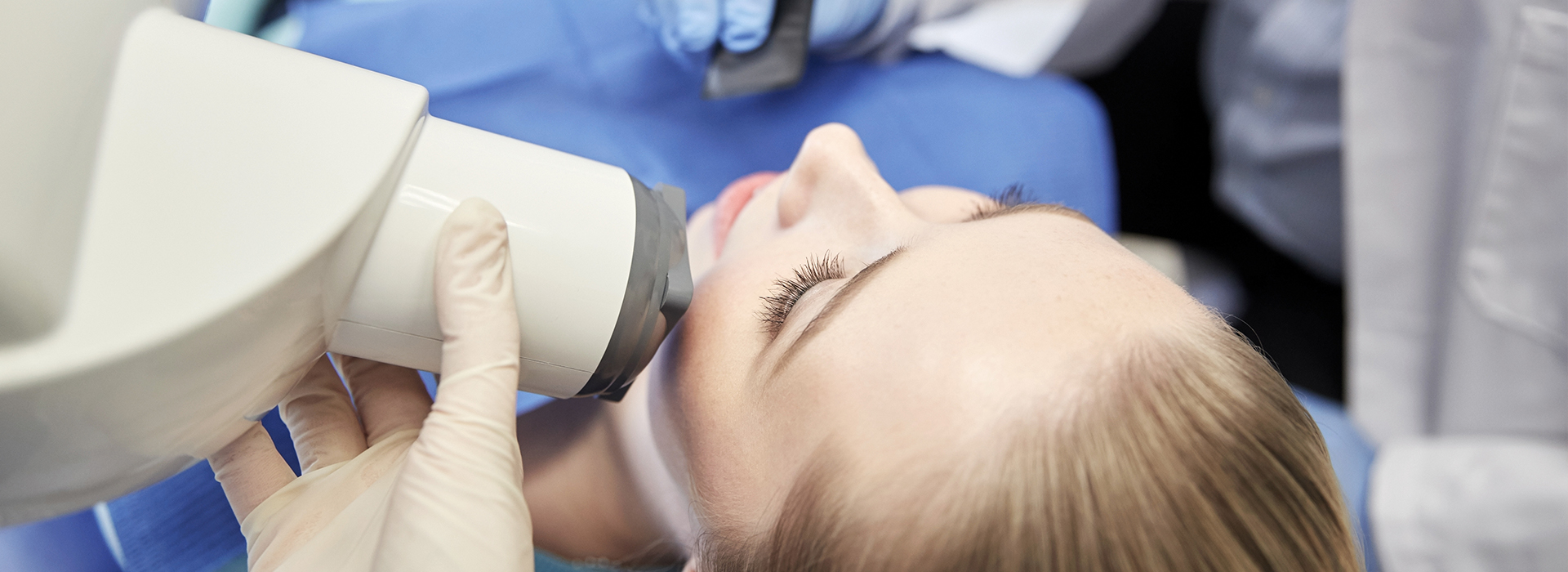
Digital radiography replaces traditional film with compact electronic sensors that detect X‑ray energy and translate it into a high-resolution image almost instantly. Unlike chemical development, the image appears on a computer monitor in seconds, so both patient and clinician can review it together during the appointment. The process is straightforward: the sensor is positioned inside the mouth or beside the head, an exposure is made, and the resulting image is immediately available for viewing and adjustment.
Because the sensor converts information into digital data, images can be enhanced with software tools that improve contrast, magnify details, and measure distances precisely. These adjustments help clinicians spot early signs of decay, bone loss, or other conditions that might be difficult to see on untreated film. The clarity and flexibility of digital files make them a valuable diagnostic asset across routine exams and more complex restorative planning.
For patients, the experience is more comfortable and less time‑consuming than traditional X‑ray procedures. There is no darkroom or waiting for film to develop, and the quick feedback allows dentists to explain findings in real time, using visuals to support treatment discussions. This immediacy improves understanding and helps patients make informed decisions about their care.
Instant access to crisp, adjustable images changes how clinicians approach diagnosis. With digital radiography, staff can manipulate brightness, contrast, and magnification to better visualize subtle changes in tooth structure and supporting bone. These enhancements make it easier to identify small cavities, hairline fractures, and early periodontal concerns that might be missed on conventional film.
Beyond visual tweaks, many practices integrate image analysis tools that assist with measurements and comparisons over time. Side‑by‑side viewing of current and prior images supports more accurate monitoring of disease progression or healing after treatment. This continuity of data creates a clearer clinical narrative and supports evidence‑based treatment planning for patients of all ages.
Digital files also lend themselves to interdisciplinary collaboration. When specialists or lab technicians need to review an image, the digital format allows for rapid transfer without loss of quality. Faster consultations mean quicker diagnostic conclusions and a more coordinated approach to care, which ultimately benefits the patient’s treatment timeline and outcomes.
One of the most commonly cited advantages of digital radiography is the reduced radiation exposure compared with older film techniques. Digital sensors are more sensitive to X‑rays, so they require smaller doses to produce diagnostically useful images. For patients who need periodic monitoring, such as children, orthodontic cases, or individuals with chronic conditions, lower cumulative exposure is an important safety consideration.
Practices using digital radiography still adhere to established radiation protection principles—keeping doses “as low as reasonably achievable” while obtaining the diagnostic information needed. Shielding, proper positioning, and modern imaging protocols all work together to protect patients and staff. Clear communication about these safety measures helps patients feel reassured about the imaging process.
Additionally, the speed of capture reduces the need for retakes. Because clinicians can verify image quality right away and make adjustments on the spot, fewer repeated exposures are required. That efficiency contributes to both safety and a smoother visit for patients who may be anxious or have difficulty holding still for extended periods.
Digital radiographs integrate seamlessly into electronic health records, creating a centralized repository for each patient’s imaging history. This organization simplifies charting, follow‑up, and long‑term comparisons while supporting a more holistic view of oral health. When images are stored as standardized digital files, clinicians can access them quickly during appointments or when planning complex procedures.
Secure transmission protocols allow clinicians to share images with specialists, insurance providers, or labs without compromising quality. Sharing is accomplished through encrypted channels, preserving patient privacy while enabling timely consultations. In urgent cases, rapid access to high‑quality images can accelerate decision‑making and help coordinate care across providers.
For patients who relocate or change providers, digital records reduce friction. Images can be transferred electronically upon request, maintaining continuity of care and providing receiving clinicians with the full diagnostic context. This interoperability supports better outcomes and demonstrates a practice’s commitment to modern, patient‑centered systems.
Digital radiography streamlines the clinical workflow in tangible ways. Technicians and clinicians spend less time on film handling and development and more time on patient care and interpretation. Faster imaging translates to shorter visits and improved scheduling flexibility, benefiting both busy families and the practice team. Administrative tasks tied to physical film—storage, archiving, and retrieval—are eliminated or greatly reduced.
There are also environmental benefits to consider. Because no chemical developers or fixed solutions are needed, digital imaging reduces hazardous waste and the associated handling concerns. Eliminating film and processing materials contributes to a smaller ecological footprint for the office and aligns with broader efforts to run more sustainable healthcare operations.
Finally, adopting digital radiography positions a dental practice to leverage future advances in imaging and software. As image analysis, 3D integration, and artificial intelligence tools evolve, digitally captured images provide a foundation for adopting new capabilities without overhaul. This forward compatibility ensures that investments in technology continue to deliver clinical value over time.
In summary, digital radiography offers patients and clinicians a safer, faster, and more flexible approach to dental imaging. By combining lower radiation doses, immediate image availability, secure storage, and environmental advantages, it enhances diagnostic confidence and improves the overall patient experience. If you have questions about how digital X‑rays are used during your visit or would like more information about our imaging protocols at ProSmiles OC, please contact us for more information.
Digital radiography uses compact electronic sensors to capture X‑ray energy and convert it into high‑resolution images displayed on a computer almost instantly. Unlike film, the image appears in seconds so patients and clinicians can review findings together during the visit. This immediate feedback supports clearer explanations and faster decision making.
Because the sensor records information as digital data, images can be enhanced, measured and stored without chemical processing. The workflow is faster and generates less hazardous waste than traditional film development. These differences make digital radiography a practical, patient‑centered upgrade for routine exams and more complex treatment planning at ProSmiles OC.
During an exam a small intraoral sensor or an extraoral plate is positioned in or outside the mouth and a brief exposure is made to capture the image. The process is quick and requires minimal patient cooperation, with the clinician able to view the image immediately for quality and diagnostic value. If an image needs adjustment, the technician can reposition the sensor and retake it right away, reducing overall time in the operatory.
Different sensor types and imaging angles are used depending on the diagnostic need, including bitewing, periapical and broader extraoral views. Each capture is tailored to visualize specific teeth, supporting structures or full arches when necessary. This adaptability helps clinicians gather the right information without unnecessary exposures.
Digital sensors are more sensitive to X‑rays, which allows diagnostically useful images at lower radiation doses than conventional film. Dental practices follow established radiation protection principles to keep doses as low as reasonably achievable while obtaining the information needed. Standard precautions such as proper positioning, shielding and collimation further reduce exposure for patients and staff.
Because images appear instantly, clinicians can verify image quality immediately and avoid repeat exposures whenever possible. Special attention is given to patients who require periodic monitoring, such as children or those with ongoing conditions, to minimize cumulative dose. Clear communication about safety practices helps patients feel reassured about the imaging process.
Digital images can be adjusted for brightness, contrast and magnification, which helps clinicians detect subtle changes such as early decay, hairline fractures and initial bone loss. These software enhancements reveal diagnostic details that might be difficult to see on untreated film. As a result, clinicians can identify problems earlier and recommend appropriate preventive or restorative care.
Digital files also make it easy to compare current and prior images side by side, supporting accurate monitoring of disease progression or healing after treatment. Measured comparisons and integrated image tools strengthen evidence‑based planning for restorations, implants and other procedures. The continuity and clarity of digital records contribute to more predictable treatment outcomes.
Yes. Modern imaging software offers tools to enhance contrast, apply filters, measure distances and mark areas of interest to support clinical interpretation. These tools help highlight anatomy, quantify bone levels and refine assessments for restorative or surgical planning. Enhanced visualization is particularly helpful when evaluating fine structural changes that influence treatment decisions.
Some practices also use image analysis features that assist with longitudinal comparisons and objective measurements, but the clinician remains responsible for final interpretation. Digital files are compatible with evolving technologies, including 3D integration and advanced analysis tools, which expand diagnostic capabilities over time. This flexibility helps keep a practice clinically current without repeatedly replacing core imaging equipment.
Digital radiographs are stored as electronic files within a patient’s chart, creating a centralized imaging history that simplifies follow‑up and long‑term comparisons. Standardized file formats allow high‑quality images to be retrieved quickly during appointments or exported for consultation. Centralized storage reduces the administrative burden of physical film handling, archiving and retrieval.
When images are shared with specialists, laboratories or a new provider, secure transmission protocols are used to protect privacy and maintain image quality. Electronic transfers preserve diagnostic detail and support coordinated care across providers. Patients who change providers can request electronic copies, which helps preserve continuity of care without degrading image information.
Patients can expect a quick and minimally invasive process that usually takes only a few moments per image. The clinician or assistant will position the sensor, make a brief exposure and review the image on screen to confirm quality. Because images appear immediately, the clinician can explain findings using visuals while the patient is still in the chair.
There is generally less waiting than with film‑based systems and fewer repeat exposures due to instant quality checks. Patients who feel anxious or have difficulty holding still will often appreciate the faster workflow. Staff members are available to answer questions and explain how images relate to recommended care.
Digital radiography’s lower required doses and rapid capture make it well suited for children, who may need more frequent monitoring during growth and development. The ability to take quick, clear images helps clinicians track tooth eruption, detect early decay and monitor the health of supporting bone with minimal discomfort. Shorter imaging times also reduce anxiety for younger patients and make appointments more efficient for families.
For orthodontic evaluation and treatment planning, digital images provide precise records that can be compared over time and integrated into broader diagnostic workflows. High‑quality images assist in assessing tooth position, root alignment and jaw relationships that inform appliance selection and timing. These capabilities support safer, more predictable pediatric and orthodontic care.
Digital radiography eliminates the need for chemical developers and film processing, reducing hazardous waste and the environmental footprint associated with traditional imaging. This change removes the need to handle and dispose of processing chemicals and film, which simplifies office operations and supports sustainability goals. Practices can reduce storage space and administrative tasks related to physical film archiving.
Operationally, digital imaging speeds workflow by cutting time spent on film handling and development, allowing clinical staff to focus more on patient care. Faster imaging contributes to shorter appointments and improved scheduling flexibility for patients. The digital format also enables easier adoption of future imaging advances, helping offices maintain clinical relevance over time.
Practices that use digital radiography offer patients faster, clearer imaging with lower radiation exposure and more efficient appointments. Digital images enhance diagnostic confidence and enable better communication between the clinician and patient, supporting informed treatment decisions. Choosing a digitally equipped practice demonstrates a commitment to modern, evidence‑based care and patient comfort.
At ProSmiles OC the team couples advanced imaging technology with a focus on patient comfort and practical communication, so you can see and understand findings in real time. If you have questions about how digital X‑rays are used in your care or about our imaging protocols, our staff will gladly explain what to expect and how images support your treatment plan.
